Anti Hbs (Mikropartikül Immün Assay-Meia Veya Benzeri) – As we all know that it is Turkish version of anti hbs (microparticle immunoassay-meia or similar). We are going to write an article on this for the people who need English article on anti hbs (microparticle immunoassay-meia or similar).
What is Anti HBs?
Hepatitis B virus is a DNA virus have its place to the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus contains various proteins with antigenic properties. One of these is the S protein, which is located on the surface of the virus and originates from the first letter of the English word ‘surface’. The way to understand whether antibodies have formed in the body against this protein structure is to look at the Anti HBs value in the blood.
What Does Anti HBs Positive Mean? (Anti RLS Height)
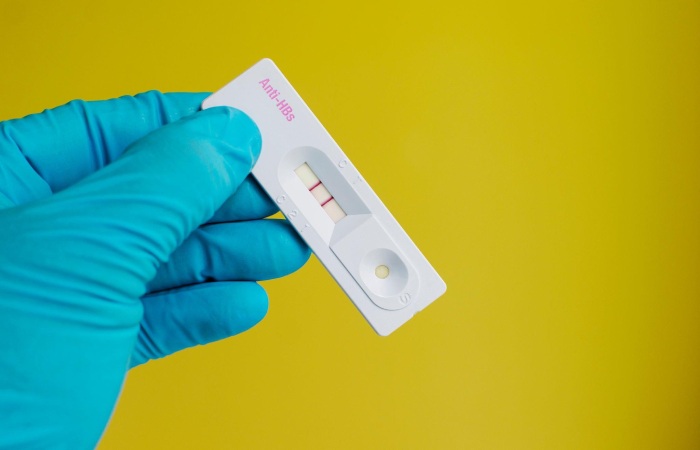
Anti HBs positive (anti HBS high) is an indicator that the person is generally protected against Hepatitis B virus infection, including its value in the blood . Hepatitis B virus causes symptomatic/asymptomatic acute viral hepatitis B virus infection after entering the body. If a positive Anti HBs test is detected in the blood of a person who develops acute viral hepatitis B virus infection within 6 months at the latest, this is an indication that the disease has been cured. In other words, if a person exposed to Hepatitis B virus infection is detected as positive for Anti HBs in the blood after a while (within 6 months at the latest), this situation; It shows that you have recovered from hepatitis B virus infection and are protected against it, you will not get the disease again and you are no longer contagious.
Anti HBs positivity can also be achieved without contracting the disease. This is achieved by completing the doses within the framework of the vaccination scheme with existing vaccines against the Hepatitis B virus. Because the aim of the vaccine is to ensure the formation of antibodies (Anti-HBs) against the S protein of the Hepatitis B virus. However, for this to happen, it must first be shown that the person has not encountered the Hepatitis B virus.
Antibody (anti HBs) against the S protein of the Hepatitis B virus occurs either after a certain period of time (at least 6 months) has passed against the Hepatitis B virus that enters the body after being infected with the disease, or as a result of the administration of Hepatitis B virus vaccines to protect against getting sick against Hepatitis B. . Anti-HBs may not develop in anyone who has the disease or is vaccinate with Hepatitis B vaccines, that is, it may not become reactive. This situation;
- It is an indication that the disease is not cure in people infected with the disease and that the disease has become chronic (after 6 months or more). Such people transmit the disease to others through blood, various body fluids and tissues. In addition, over time, some of such people become candidates for the development of liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- It is an indication that the desired effect of vaccination is not achieved in people vaccinated to protect against the disease and also that protection against Hepatitis B is not provide.
What Should be the Normal Anti HBs Value?
“What should be the anti HBs value?” The answer to the question can explained as follows: An Anti-HBs value of ≥10 mIU/mL in the blood, both after experiencing the disease and after the vaccination program, is an indicator of the formation of antibodies at a protective level. It is not desirable for the value to be below this level, that is, <10 mIU/ml. It should kept in mind that in a person whose anti-HBs value is detect at 10 mIU/ml and above (10 – 100 mIU/ml), it may decrease to <10 mIU/ml over the years. In such cases, a dose reminder Hepatitis B vaccine administration may be necessary.
“What does Anti HBs 1000 mean?” The answer to the question can be given as follows: When talking about the protectiveness of the anti-HBs value, there is no difference between the value being at any value above ≥10 mIU/mL and this value reaching 1000 mIU/mL. This indicates the amount of antibodies formed against the virus entering the body. However, an Anti-HBs value of ≥10 mIU/mL indicates an adequate level of protection.
What Does Anti HBs Negative Mean?
Anti-HBs alone does not provide sufficient information when evaluating hepatitis B virus infection serologically. While this is being evaluate, other serological tests for the Hepatitis B virus are also evaluate together. When evaluated together, the Anti HBs negative result explains a situation in which the Hepatitis B virus has never been encounter before and has not infected, but it can also indicate a situation in which the virus has encountered before but cannot be cleare from the body, has become chronic and continues to contagious. It is possible to understand this situation by evaluating both the patient’s history and serological tests.
Hepatitis B Virus Infection
The infectious disease caused by the Hepatitis B virus is common around the world. Transmission of the virus is often; from an infected mother to the baby during birth, as a result of sexual intercourse with an infected person, through contact with blood and body fluids containing the virus and damaged skin and mucosa, or as a result of shared use and intravenous application of a needle containing infected blood and body fluids, as in drug addicts. occurs. Apart from this, the use of infected medical instruments or some shared tools and equipment without sterilization also leads to the transmission of the Hepatitis B virus.
After the virus enters the body, the target organ is the liver. Once there, it causes acute and chronic infectious diseases. It is estimate that nearly 300 million people in the world live with chronic Hepatitis B virus infection, and an average of 1.5 million people infected with Hepatitis B virus every year. Unmonitored chronic Hepatitis B virus infections result in the development of cirrhosis and liver cancer over time. This situation is life-threatening.
The diagnosis of hepatitis B virus infection made by evaluating the patient’s complaints, physical examination findings and laboratory tests together. After the virus enters the body as mentioned above, it first causes acute viral Hepatitis. This condition causes 90 percent of complaints in children and adults over the age of 5 and results in the virus being clear from the body within 6 months. The development of chronic viral Hepatitis B infection in these age groups is 10 percent. In those who contract the disease in infancy, 90 percent of acute viral Hepatitis B is asymptomatic. By the age of 5, therefore infection becomes chronic in 20 percent of them.
The most common complaints in symptomatic acute viral Hepatitis B infection are
- Weakness, tiredness, exhaustion
- Anorexia
- Slight increase in normal body temperature (up to 38 degrees)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Darkening of urine color
- Yellowing of the body, skin and eyes
- Muscle and joint pain
Rarely, acute liver failure may develop during the course of acute viral Hepatitis. In such a case;
- change of consciousness,
- An increase tendency to bleeding may be observe.
The most typical finding in the examination of patients with acute viral Hepatitis B infection is liver size. This may be accompanied by spleen enlargement. In laboratory examinations, there is a significant increase in liver enzymes. It reaches a height of more than 10 times normal. In cases with the above complaints and physical examination findings, the definitive diagnosis is make with serology results. And also in cases of acute viral Hepatitis B infection;
- Hbs Ag Positive
- Anti – Hbc IgM Positive
- It is detect as Anti-Hbs Negative. Hbs Ag test is also positive.
In a person with acute viral Hepatitis B infection, symptoms may continue for weeks, sometimes months. And In 90 percent of the cases, serological indicators detected within 6 months at the latest;
- Hbs Ag Negative
- Anti – Hbc Total Positive
- Anti-Hbs Positive detection is an indication that recovery from the disease has occurred.
And In a person with acute viral Hepatitis B infection, serological indicators are still higher 6 months after the onset;
- Hbs Ag Positive
- Anti – Hbc Total Positive
- If Anti-Hbs is negative, this indicates that the disease has become chronic.
In chronic Hepatitis B virus infection, cases may not have any obvious complaints. People may sometimes feel tired and weak. However, most of the complaints seen in acute viral Hepatitis B are absent. The disease develops in 4 different processes, respectively.
These; immune tolerance period, immune active period, immune elimination period and reactivation period. These periods detected by serological tests, and also their detection is important in determining whether treatment required. For this reason, people diagnosed with chronic Hepatitis B virus infection should followed up at regular intervals. In prolonged cases where this not done and treatments not applied when they should treated. The development of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer encountered. Serological tests;
- Hbs Ag Negative
- Anti – Hbc Total Negative
- People who found to be Anti-Hbs Negative mean that they have never encountered the Hepatitis B virus.
Such people should protected against Hepatitis B infection by vaccination. In normal healthy individuals, 3 doses of Hepatitis B vaccine required at regular intervals to provide protection against the Hepatitis B virus. After vaccination, whether the body has protection against the Hepatitis B virus evaluated according to the results of the Anti-Hbs test.
After the vaccinations completed, if the serology result is Anti Hbs positive and the level is ≥10 mIU/mL, this indicates that the person protected against Hepatitis B virus. In other words, even if the body of such a person infected with the Hepatitis B virus. The virus that enters the body will neutralized thanks to the existing antibodies (Anti Hbs) and will not be able to enter the cell and also cause disease.
